A muscle contraction can be defined by the change in muscle length that occurs, following a contraction within the muscle.
The contraction occurs following the activation of individual motor units within the muscle. Once activated these innervate the associated muscle fibres, causing a contractile force within the muscle. As a consequence, the muscle contraction will result in either:
- A change in muscle length (lengthening or shortening) – referred to as an Isotonic contraction
- Remain the same length – referred to as an Isometric contraction.
Isotonic Muscle Contraction
An isotonic contraction occurs when a muscle changes length while contracting under a constant tension. While we often think of a muscular contraction resulting in a muscle shortening, it can also lengthen – depending on the force being resisted. As such there are two types of isotonic contraction:
- Concentric (muscle shortens)
- Eccentric (muscle lengthens)
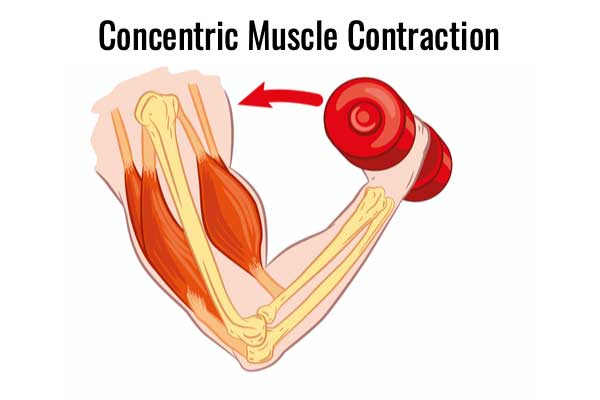
Concentric Contraction
A concentric muscular contraction occurs when a muscle shortens in length, while overcoming a resistance or load. In this case, the muscle exerts more force than the resistance, or load, that it’s working against. This results in a shortening of the muscle as well as a change in the angle of the joint.
Examples of concentric muscular contractions include:
- Lifting a dumbbell during a bicep curl. Here the bicep brachii contracts concentrically, working against gravity, to lift the dumbbell. As the bicep muscle shortens it pulls on the bones of the forearm, decreasing the angle at the elbow and lifting the weight upwards and towards the shoulder joint.
- Another example is the quadricep muscles when walking up the stairs. In this case the quadriceps contracts concentrically to overcome gravity and increase the angle at the knee.
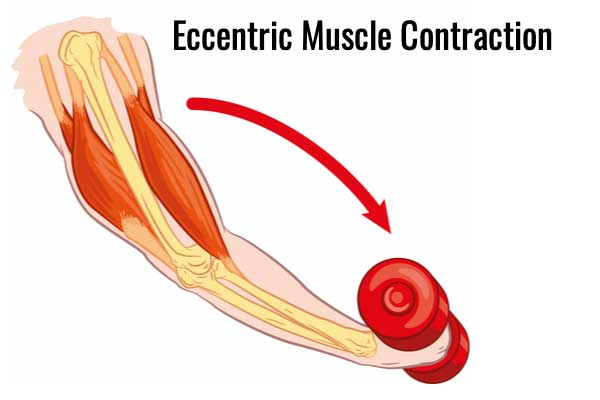
Eccentric Contraction
Eccentric muscle contractions occur when a muscle/muscle fibre lengthens while under tension. This type of contraction normally occurs against gravity such as the lowering phase of a bicep curl, or pull-up.
Eccentric contractions are known to have greater force production. In practical terms, this allows you to lower heavy weights in a controlled manner.
In effect, they act like a breaking force, allowing movement to occur in a controlled way, by counteracting and eliminating acceleration (from gravity) and helping to protect joints from injury.
The greater force production occurs due to increased recruitment of type II (fast twitch muscle fibres).
Despite this, eccentric contractions actually result in a lower level of recruitment of motor units. For this reason, high levels of eccentric contractions can cause temporary reductions in muscle strength, efficiency, and lead to increased muscle damage (micro-traumas) and delayed onset muscle soreness.
Importantly, these effects are temporary and once recovered (approximately 48hrs) we see increased strength, fatigue resistance and protection against DOMS. In fact, eccentric strength training is known to be an effective way to develop maximum strength and sports performance. In part, this is due to adaptations that occur following the muscle fibre damage – repair and muscle hypertrophy – as well as improved neuromuscular coordination.
Examples of eccentric muscular contractions include:
- Lowering a dumbbell during a bicep curl. Here, the bicep brachii contracts eccentrically to lower the dumbell in a controlled manner.
- Another example is walking down the stairs or running downhill. During downhill running the quadriceps contract eccentrically in order to control the movement, resist the force of gravity and prevent your knee collapsing.
One downside to the use of eccentric training is that it can result in a greater risk of injury. It can also cause increased levels of inflammation.
Isometric Muscle Contractions
Isometric contractions occur when a muscle contracts without shortening or lengthening. In this case, the force exerted by the muscle is equal to the force that it’s resisting. Consequently, the muscle remains the same length.
Isometric contractions don’t just happen in muscle’s responsible for movement, they also occur in stabilising, or fixator muscles.
One point to note: unlike with dynamic (isotonic contractions) – where strength training leads to increased strength throughout the joint angle; with isometric contractions strength is only increased in the joint angle that is worked.
Examples of isometric contractions include:
- Postural muscles working to maintain body posture. Such as the core muscles when performing the plank exercise, or the stabilising muscles when running.
- Pushing against an immoveable object such as wall, or a static rugby scrum.
- Holding, or carrying an object in static position – carrying a shopping bag, holding a dumbbell in a fixed position.

One important consideration with this type of muscle contraction is that it can lead to a rapid rise in blood pressure.
Isokinetic Muscle Contractions
Isokinetic muscle contractions occur when a muscle contracts and shortens at a constant speed, or constant angular speed. To perform Isokinetic muscle contractions requires specialist equipment – known as an Isokinetic Dynamometer. This increases the load when it senses the muscle is speeding up, ensuring that the speed of movement is held constant throughout.
Benefits of Isokinetic Muscle Contractions:
- Isokinetic exercises can be used to replicate sport-specific speeds. As such, they allow you to develop strength at the same speed of movement used during a specific sport. This is believed to lead to improvements in neuromuscular coordination, increasing the recruitment of muscle fibres and improving neuromuscular efficiency. A good example is an isokinetic stationary bike that controls the speed to a set number of revolutions per minute.
- Isokinetic muscle contractions can lead to more even gains in muscle strength, throughout a muscles entire range of movement. This is due to the way tension is at its maximum throughout the muscles range of movement.
- Another benefit of controlling the speed of movement, is a reduced risk of injury. This is particularly important during periods of rehabilitation following injury or surgery.
- Can lead to improved strength, muscular endurance, cardiac fitness, and may also have a positive effect on core muscles.
